Water ionizers are marketed for commercial and home use. These devices use a process called electrolysis1 to produce four main types of electrolyzed waters called functional waters.2
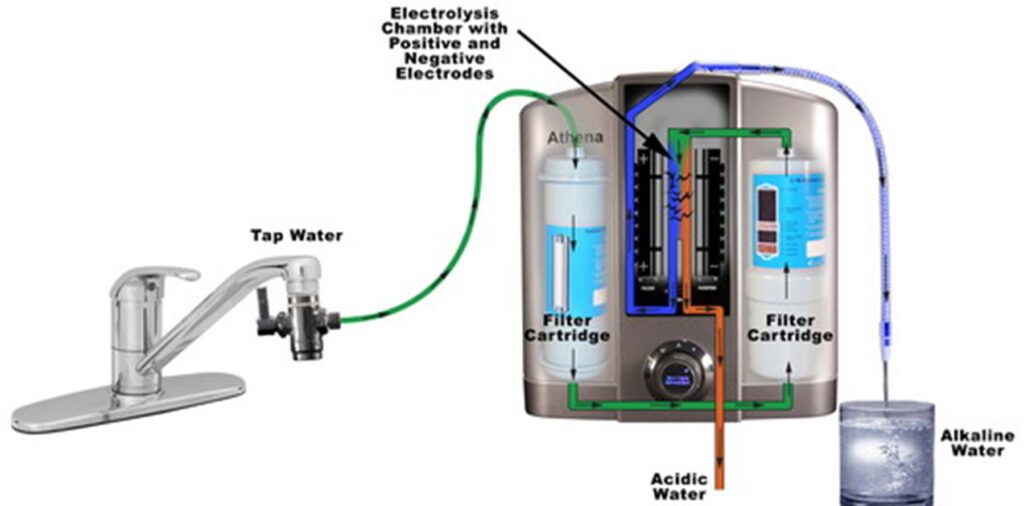
Figure 1. Depiction of a typical water ionizer connected to a tap water, producing acidic and alkaline water.
- Mildly alkaline water for drinking
- Mildly acidic water for beauty purposes
- Strong alkaline water for cleaning
- Strong acidic water for cleansing
MEDICAL DEVICE
In 1965, the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare (JMHLW) approved water ionizers as a “medical substance generator” (which could help with gastrointestinal symptoms) 3 under the Pharmaceutical Affairs Law4. Currently, in order to manufacture and/or sell water ionizers, companies must obtain certified approval by the JMHLW.5 There are at least eighteen different water ionizer companies that have been approved and certified by the JMHLW. These devices have also been certified by the Korean FDA for similar reasons, and this certification is also required in order to sell water ionizers in Korea.
*click here to learn about the history
HOW WATER IONIZERS WORK
Water ionizers produce alkaline water containing dissolved molecular hydrogen at the cathode (the negative electrode) and acidic water at the anode (the positive electrode).2 Water ionizers are plugged into the AC outlet, the power is then transformed to direct current (DC) so that electrolysis can be performed. Electrolysis alone does not change the pH of the water;6 however, most of these devices contain a basic semi-permeable ion-exchange membrane, which prevents the catholyte (with the alkaline OH- ions) and anolyte (with the acidic H+ ions) compartments from mixing together;2 thus producing alkaline (mild or strong) and acidic (mild or strong) water at the cathode and anode, respectively.
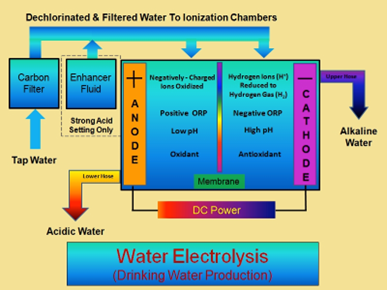
Figure 2. Schematic of how an ionizer works. Tap water is filtered, a salt solution may be added for strong alkaline and acidic waters, electrolysis is performed and the various waters are produced.
When tap water is the sole source of ions, the water ionizer will produce a mildly alkaline pH (8-11) with a negative ORP (-50 to -750) at the cathode and a mildly acidic pH (4-6) with a positive ORP (+350 to + 750) at the anode.1 *These numbers very depending on the machine, the pH, and ion/mineral content in tap water.
The process of producing alkaline and acidic water is relatively simple. The H+ ions (acid) are attracted to the negatively charged cathode where they are converted to molecular hydrogen (H2) according to the equation: 2e- + 2H+ –> H2. Because pH is the concentration of the H+ ions, and the amount of H+ ions are being decreased (converted to H2) the pH increases thus making the water alkaline. (Note: pH is logarithmic, so a decrease in H+ concentration is an increase in pH.)
At the other electrode, the hydroxide (OH–) ions are attracted to the positive anode where they are oxidized to form H+ ions. Because pH is a measurement of the concentration of H+ ions, and the amount of H+ ions is being increased, the pH decreases thus making the water acidic. (Note: pH is logarithmic, so an increase in H+ concentration is a decrease in pH.)
*Learn more about electrolysis
MINERAL CHANGES IN TAP AND ELECTROLYZED WATER
Generally the concentration of the minerals in the acidic or alkaline water is the same as the source water. Many claim that the “beneficial alkaline minerals” are increased in the alkaline water and that all the “bad minerals and toxins, (e.g. fluoride, THMs, etc.)” are eliminated in the acidic water. This of course is not true and is greatly prevented by the membrane, which separates the two compartments.
However, in very soft water areas addition of an electrolyte, such as calcium, is required for effective electrolysis. Obviously adding more minerals will result in more minerals in the alkaline water. This is often the case in Japan and is perhaps how the idea that alkaline water has more minerals in it than the source water began.
TYPES OF WATER IONIZERS


There are many different types water ionizers. Most of them are set up to separate the acidic and alkaline waters called continuous type; however, others allow the H+ ions to mix with the alkaline side, which makes only one out-put hose7. Electrolyzer devices that are made specifically for the strong acidic water production are called “bleach generators” and have been a around for many years and are increasing in popularity.
ELECTRODE MATERIAL

The material that the electrodes are made out of is very important, as this not only increases the efficiency of electrolysis,8 but it can also contaminate the water. Corrosion, oxidation and degradation of the electrodes are common problems with electrolysis (see pic.). Most water ionizers use platinum coated titanium electrodes. Platinum is very inert and thus does not react with the electrolytes or products during electrolysis.9 This also increases the longevity of the machine. As seen in the picture, the electrodes undergo deterioration, which may adversely affect one’s health. 10
Read about How to Get Molecular Hydrogen